The speed ratio of the reducer refers to the ratio of the speed of the output shaft of the reducer to the speed of the input shaft. In the engineering field, the speed ratio of the reducer is a very important parameter, which directly affects the output torque, output power and working efficiency of the reducer. The selection of reducer speed ratio has an important impact on the design and performance of the mechanical transmission system.
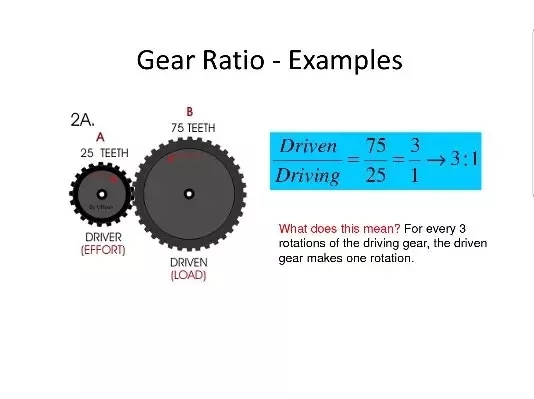
The speed ratio of the reducer is usually represented by two numbers, such as 5:1, 10:1, etc. These two numbers respectively represent the ratio of the speed of the output shaft of the reducer to the speed of the input shaft. For example, if the speed ratio of a reducer is 5:1, then when the input shaft speed is 1000 rpm, the output shaft speed will be 200 rpm.
The selection of the speed ratio of the reducer needs to be determined based on the specific work requirements and the design of the transmission system. Generally speaking, a larger speed ratio can provide greater output torque and is suitable for applications that require greater output power and lower speed; while a smaller speed ratio can provide higher output speed and is suitable for applications that require High speed but low output power.
In actual engineering applications, the selection of reducer speed ratio needs to consider multiple factors, including but not limited to the following points:
1. Output power and speed requirements: Determine the required output power and speed range based on specific work requirements, and then select the appropriate speed ratio to meet these requirements.
2. Torque transmission: Determine the required output torque according to the load characteristics and working environment of the transmission system, and select the appropriate speed ratio to achieve the required output torque.
3. Efficiency and lifespan: Different speed ratios will affect the efficiency and lifespan of the reducer. These factors need to be considered comprehensively to select the appropriate speed ratio.
4. Space and weight restrictions: In some special working environments, there may be restrictions on the size and weight of the reducer, and an appropriate speed ratio needs to be selected to meet these restrictions.
5. Cost consideration: Different speed ratios will also have an impact on the manufacturing cost and use cost of the reducer. Cost factors need to be comprehensively considered to select the appropriate speed ratio.
In general, the selection of reducer speed ratio requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including output power and speed requirements, torque transfer, efficiency and life, space and weight constraints, and cost considerations. Reasonable selection of reducer speed ratio can effectively meet engineering needs and improve the performance and reliability of the transmission system.
Writer: Sharon
Post time: May-06-2024

