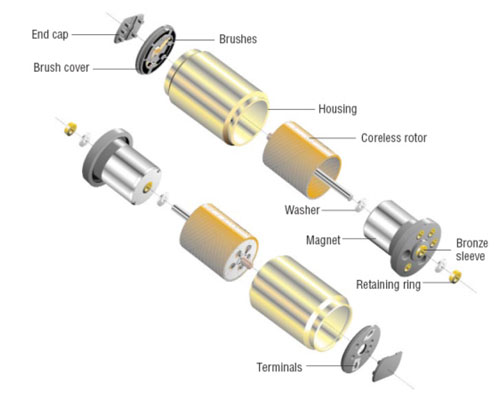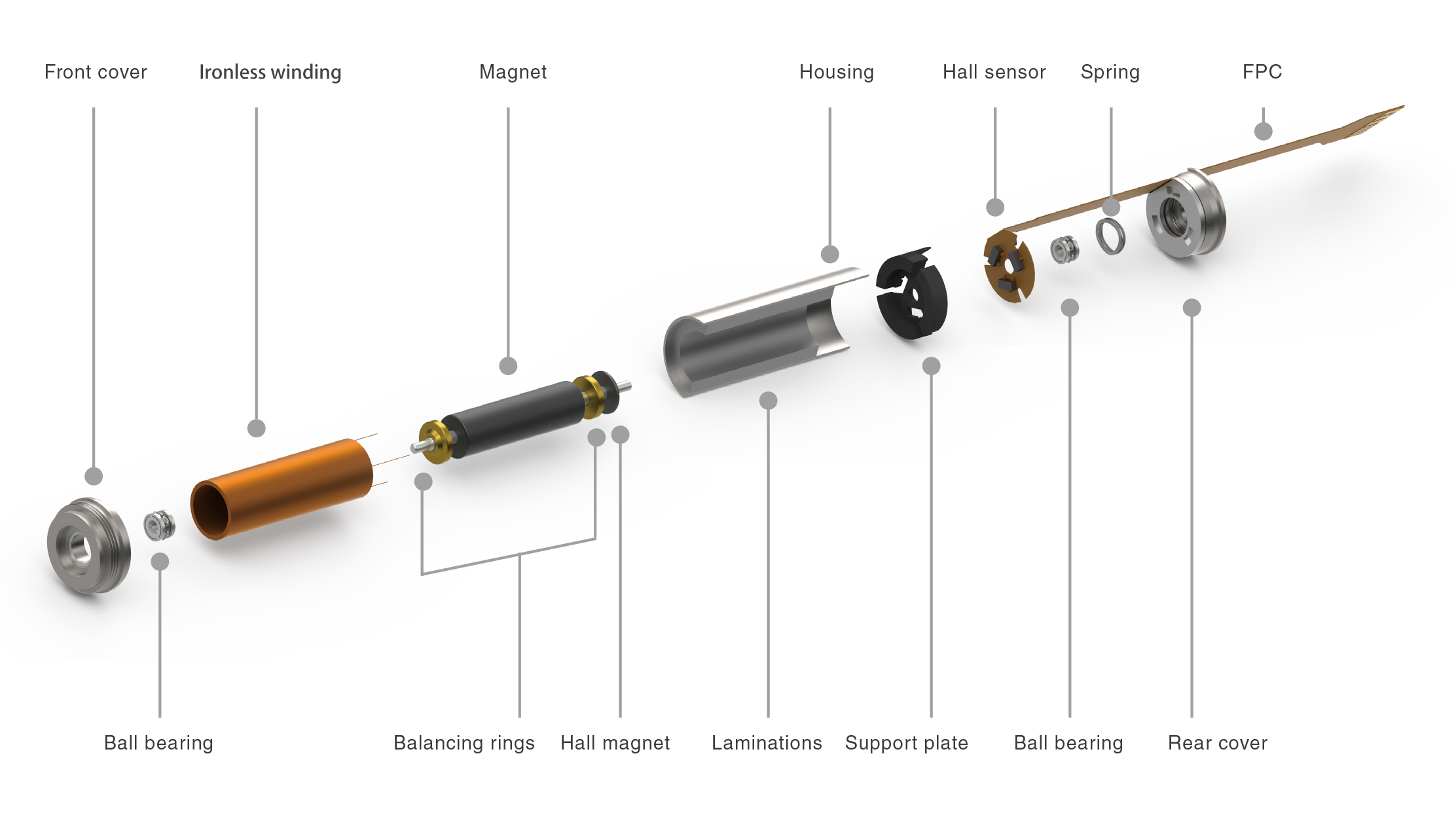
Heating is an inevitable phenomenon during the operation of the bearing. Under normal circumstances, the heating and heat dissipation of the bearing will reach a relative balance, that is, the heat emitted and the heat dissipated are basically the same, so that the bearing system will maintain a relatively stable temperature. state.
Based on the quality stability of the bearing material itself and the grease used, the bearing temperature of motor products is controlled at 95°C as the upper limit. While ensuring the stability of the bearing system, it will not have a great impact on the temperature rise of the coreless motor windings.
The main causes of heating in bearing systems are lubrication and reasonable heat dissipation conditions. However, during the actual manufacturing and operation of the motor, the bearing lubrication system may not operate well due to some inappropriate factors.
When the working clearance of the bearing is too small and the fit between the bearing and the shaft or the bearing chamber is loose, it causes running circles; when the axial fit relationship of the bearing is seriously misaligned due to the action of axial force; the unreasonable fit between the bearing and related parts causes lubrication Undesirable conditions such as grease being thrown out of the bearing cavity will cause the bearing to heat up during motor operation. The grease will degrade and fail due to excessive temperature, causing the motor's bearing system to suffer a devastating disaster in a short period of time. Therefore, whether it is the design or manufacturing process of the motor, as well as the later maintenance and upkeep of the motor, the size of the matching relationship between the parts must be controlled.

Shaft current is an unavoidable quality hazard for large motors, especially high-voltage motors and variable-frequency motors. Shaft current is a very serious problem for the bearing system of the coreless motor. If necessary measures are not taken, the bearing system may be damaged in a few seconds due to the shaft current. Disintegration occurs within ten hours or even a few hours. This type of problem manifests itself as bearing noise and heat in the early stage of the failure, followed by the failure of the grease due to heat, and within a short period of time, the problem of shaft holding due to bearing ablation occurs. For this reason, high-voltage motors, variable frequency motors, and low-voltage high-power motors will take necessary measures in the design stage, manufacturing stage, or use stage. There are two common ones. One is to cut off the circuit (such as using insulated bearings, Insulating end caps, etc.), the other is a current bypass measure, that is, using a grounded carbon brush to lead the current away to avoid attacks on the bearing system.
Post time: Apr-18-2024